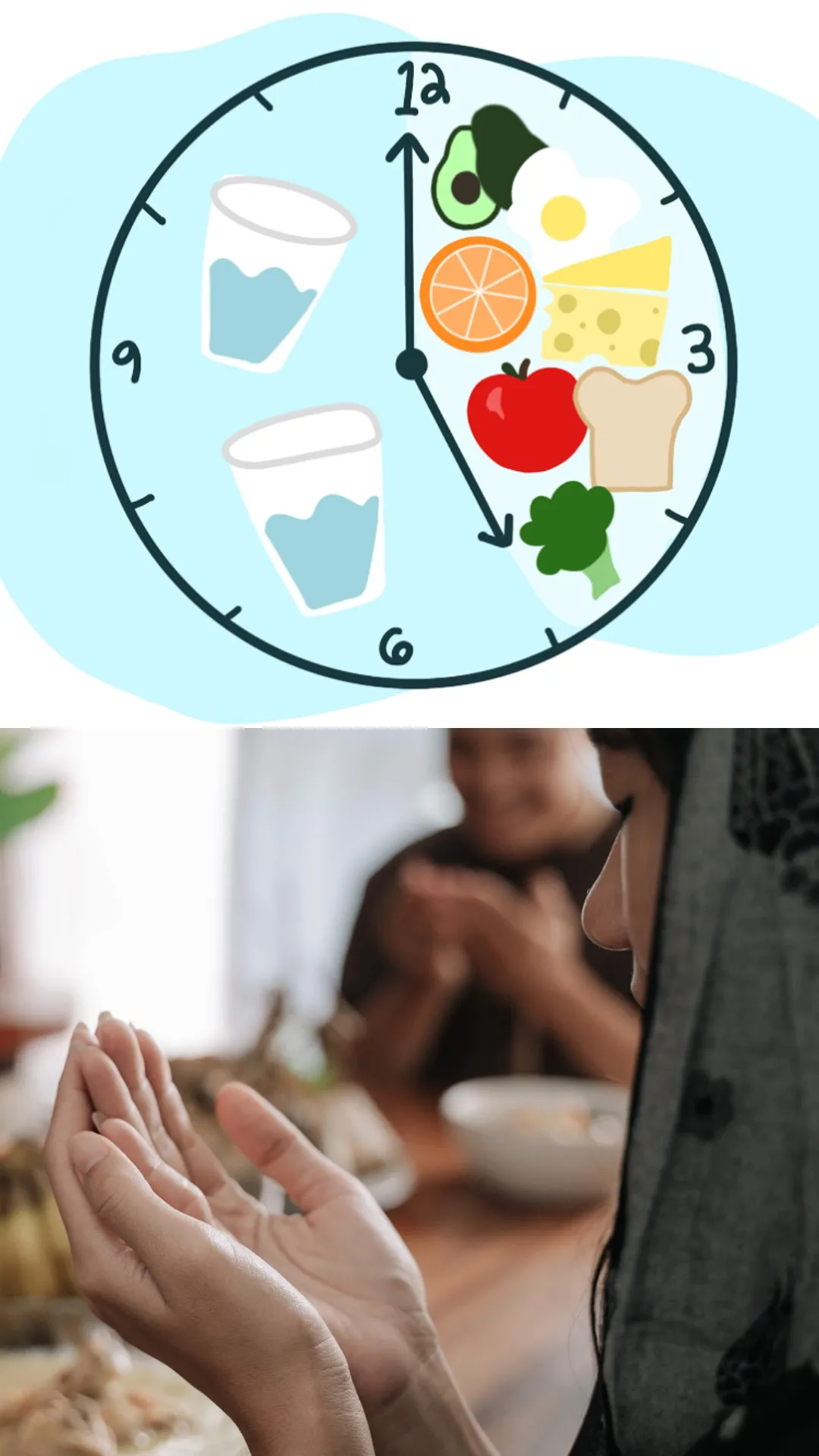


Intermittent Fasting vs Ramadan Fasting: Which is beneficial for health?
Image Source : Social

Time Structure: Intermittent fasting involves cycles of eating and fasting (e.g., 16/8 or 24-hour fasts), while Ramadan fasting is a religious practice where fasting occurs daily from dawn until sunset for a month.
Image Source : Social

Health Benefits: Ramadan fasting promotes detoxification and can enhance spiritual well-being but may lead to overeating during non-fasting hours. Intermittent fasting has been linked to improved metabolic health, weight loss, and reduced inflammation.
Image Source : Social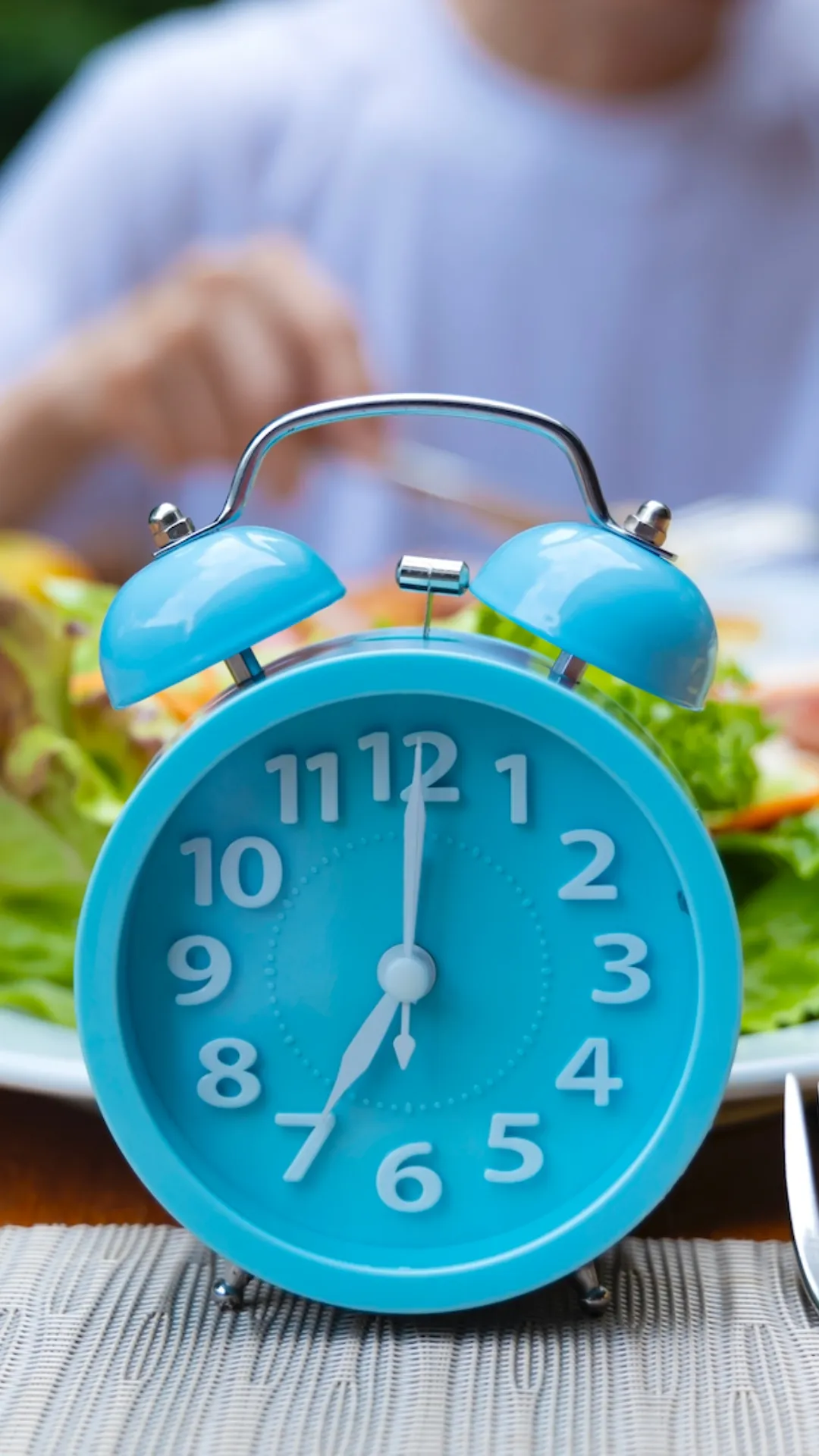
Flexibility: Intermittent fasting offers more flexibility, allowing individuals to choose their fasting windows based on their lifestyle. Ramadan fasting is fixed and follows a specific schedule during the holy month.
Image Source : Social
Physical Adaptation: Both forms of fasting can improve insulin sensitivity and heart health. However, intermittent fasting may be easier to adapt to over time, while Ramadan fasting requires significant adjustment to daily routines.
Image Source : Social
Sustainability: Intermittent fasting can be a long-term lifestyle choice, while Ramadan fasting is a short-term practice, offering a reset but not meant to be continuous throughout the year.
Image Source : Social
Next : Amla vs Aloe Vera: Which is better for hair growth?