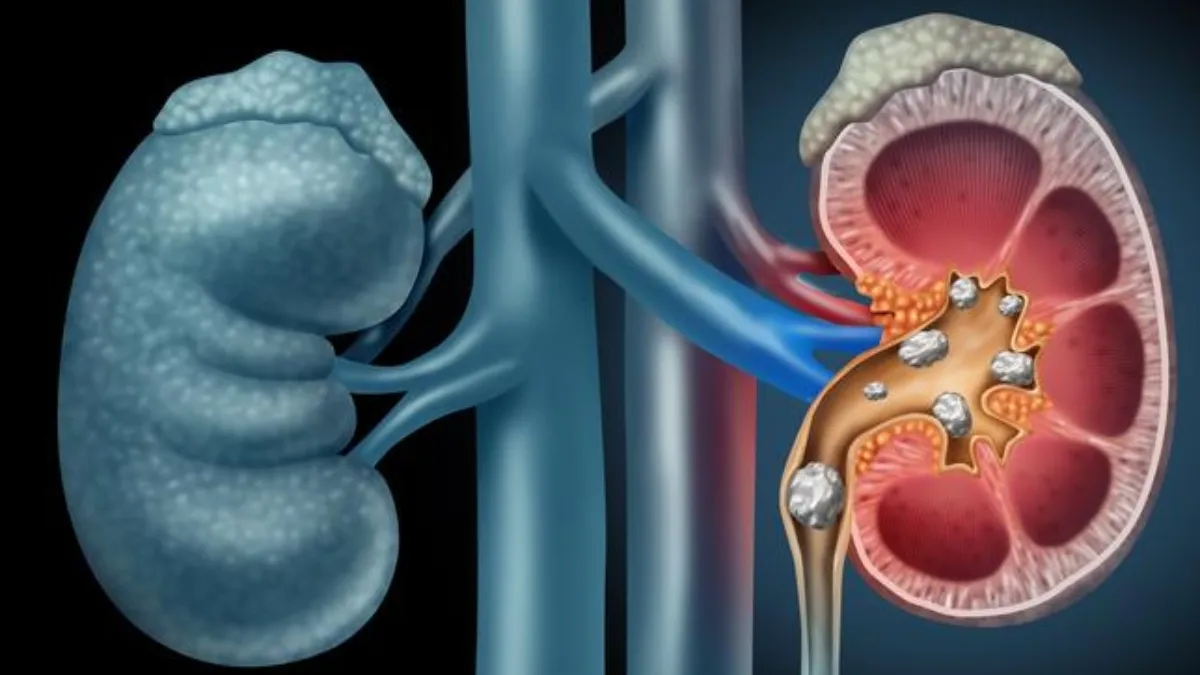
Kidney stones are increasingly common these days. They are hard mineral deposits that form in the kidneys. This is when certain substances like calcium, oxalate, and uric acid become too concentrated in the urine. The size of kidney stones can vary from person to person, They can be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a pebble. Kidney stones can cause severe pain when they pass through the urinary tract. Numerous factors can altogether contribute to kidney stones. This can include factors like dehydration, excessive salt intake, certain medical conditions, and genetics. The symptoms of kidney stones can involve intense back or abdominal pain, blood in the urine, nausea, and frequent urination. When we spoke to Dr Sachin Gupta, Consultant Nephrologist and Transplant Physician, AIMS hospital, Dombivli, he said that despite, kidney stones being so common condition, there are various myths surrounding it. These misconceptions can create confusion that can lead to poor health choices.
Myths about kidney stones
Myth: Only older people get kidney stones.
Fact: It is a common myth that kidney stones can only affect older people. It can affect people from all age groups. Factors like poor hydration, unhealthy dietary choices, and genetic makeup can contribute to the formation of kidney stones.
Myth: Drinking less water won’t cause kidney stones.
Fact: Dehydration is one of the major causes of kidney stones in most people. When you do not drink enough water then it can lead to dehydration. Insufficient water intake can cause kidney stones as your urine becomes concentrated with minerals.
Myth: All kidney stones are the same.
Fact: Not all kidney stones are the same. There are different types of kidney stones including calcium oxalate, uric acid, struvite, and cystine stones. Each type of kidney stone is caused by different factors and needs various preventive strategies.
ALSO READ: How to prevent chronic kidney disease? Expert explains causes, shares prevention tips