The border clash between the Indian Army and the Chinese People's Liberation Army (PLA) has sparked an anti-China sentiment in the country. Calls to boycott Chinese goods and reduce import from China can be heard loud and clear from up top in the political elite, to the streets next to our homes. India-China border dispute goes long back. But it is not the only border dispute China has.
China has border disputes with 18 countries that surround China from all sides. From India to Japan to The Philippines, China has on several occasions been subject of criticism by the international community over its 'expansionist policies'.
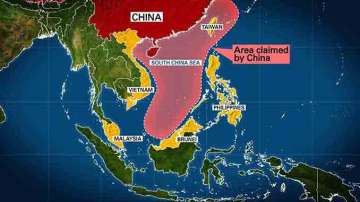
China's Border Disputes
- Japan -- Parts of South China Sea particularly Senkaku Islands, Ryukyu Islands are claimed by Japan and both countries are at loggerheads with this boundary issue
- Vietnam -- China claims large parts of Vietnam on historical precedent (Ming Dynasty, 1368-1644). Also, Macclesfield Bank, Paracel Islands, parts of the South China Sea and the Spratly Islands.
- India -- China occupies 38,000 sq km Indian territory that goes by the name Aksai Chin. It also stakes claim on Arunachal Pradesh and Ladakh. It was this expansionist policy that led to the recent clashes between the PLA and the Indian Army.
- Nepal -- China claims parts of Nepal dating back to the Sino-Nepalese War in 1788-1792. China claims they are part of Tibet, therefore part of China.
- North Korea -- Baekdu Mountain and Jiandao. China has also on occasion claimed all of North Korea on historical grounds (Yuan Dynasty, 1271-1368).
- The Philippines -- Parts of the South China Sea are contested between the two countries. The Philippines took this to the International Court of Justice, where they won the case but Chinese did not abide by the order of the ICJ.
- Russia -- 160,000 square kilometers still unilaterally claimed by China, despite China signing several agreements.
- Singapore -- Parts of the South China Sea are contested by both countries.
- South Korea -- Parts of the East China Sea. China has also on occasion claimed all of South Korea on historical grounds (Yuan Dynasty, 1271-1368).
- Bhutan -- Bhutanese enclaves in Tibet, namely Cherkip Gompa, Dho, Dungmar, Gesur, Gezon, Itse Gompa, Khochar, Nyanri, Ringung, Sanmar, Tarchen and Zuthulphuk. Also Kula Kangri and mountainous areas to the west of this peak, plus the western Haa District of Bhutan.
- Taiwan -- China claims all of Taiwan, but particular disputes are Macclesfi eld Bank, Paracel Islands, Scarborough Shoal, parts of the South China Sea and the Spratly Islands. The Paracel Islands, also called Xisha Islands in Vietnamese, is a group of islands in the South China Sea whose sovereignty is disputed among China, Taiwan and Vietnam disputes with Burma.
- Laos -- China claims large areas of Laos on historical precedent (China's Yuan Dynasty, 1271-1368).
- Brunei -- Over Spratly Islands.
- Tajikistan -- Chinese claims based on historical precedent (Qing Dynasty, 1644-1912).
- Cambodia -- China has, on occasion, claimed parts of Cambodia on historical precedent (China's Ming Dynasty, 1368-1644).
- Indonesia -- Parts of the South China Sea.
- Malaysia -- Over Parts of the South China Sea, particularly the Spratly Islands.
- Mongolia -- China claims all of Mongolia on historical precedent (Yuan Dynasty, 1271-1368). In fact, Mongolia, under Genghis Khan, occupied China.